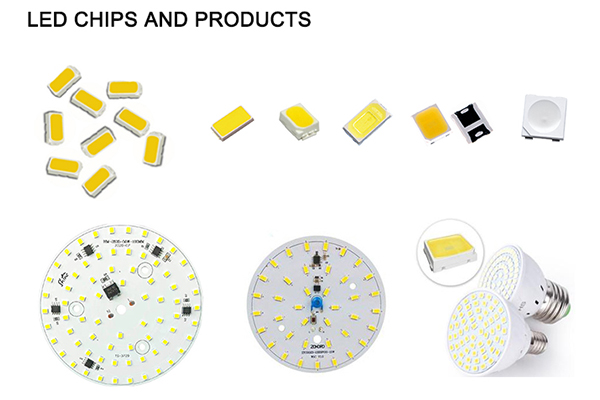
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) are solid-state semiconductor devices that convert electrical energy directly into light. At the heart of the LED is a semiconductor chip with one side bonded to the top of a reflector cup commonly called an anvil. The anvil carries a negative current. The other side of the semiconductor is connected to tiny wires commonly called whiskers, which provide positive current. The assembly is encapsulated in such a way that the top half of the epoxy encapsulation has a precise shape and acts as a lens for changing the beam angle or divergence angle.
With the advent of blue LEDs, the combination of RGB LEDs enabled new applications of LED technology in RGB-based white lighting. Coupled with more advanced intensity control full spectrum RGB LED projection came into being. The advent of blue LED technology has achieved the ultimate goal of LED development. Ultra-bright white LEDs can actually replace traditional light sources that are currently being implemented.
Characteristics and advantages of LEDs: The inherent characteristics of LEDs are undoubtedly the best substitutes for traditional light sources and provide wider applications.
Small size: LEDs are inherently tiny, and once encapsulated in epoxy, are very small and lightweight.
Long Power Consumption: LEDs consume very little power, much less than standard light bulbs, thus greatly reducing energy costs and greatly enhancing global energy savings. LEDs also require far less energy to manufacture than other light sources, further reducing the environmental impact of artificial lighting. Typically, LEDs are designed to operate at 2 – 3.6V, 0.02-0.03A, which means that LEDs typically require no more than 0.1W to operate.
Rugged: LEDs are rugged solid-state devices that are not susceptible to vibrations, such as those used in incandescent filament light bulbs.
Long Life: LEDs can enjoy a long life of up to 100,000 hours when operated under specified voltage, current and specified environmental conditions. Neo-Neon has established and adopted a newer method of evaluating LED life that is based on lumen decay over time to determine mean time between failures (MTBF).
High light efficiency and low heat generation: LEDs emit electromagnetic energy mainly in the